World Tuberculosis Day 2020: TB Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Prevention
787 viewsWorld Tuberculosis Day is observed on March 24 every year to raise awareness about Tuberculosis. Awareness about TB symptoms and treatment, risk factors, and prevention measures can have a significant impact on reducing the socio-economic impacts of the disease worldwide.
What is Tuberculosis?
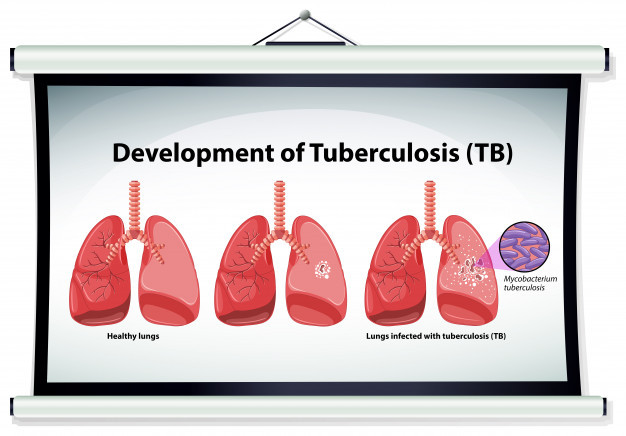
Tuberculosis (TB) an infectious disease that mainly affects the lungs but can have implications on other organs too. It can easily spread from person to person via respiratory droplets released in the air while coughing or sneezing. TB is a serious lung disease that can potentially turn fatal in some cases but it is treatable in most cases.
Tuberculosis Types
Even when the bacteria that cause TB enter your body, your immune system usually protects you from getting seriously sick. Thus, on the basis of the severity of the infection, TB can take two forms:
Latent TB (TB Infection)
If you have latent TB, bacteria have entered your body and you have contracted the TB infection. However, these bacteria stay inactive in the body. So you neither develop any TB symptoms nor is it contagious as long as the TB infection is latent. This infection can grow into TB disease if it is not treated in time.
Active TB (TB Disease)
This is a condition in which the bacteria inside your body have started multiplying and are making you fall ill, majorly by attacking your lungs. Active TB can occur a few weeks after you catch the TB infection. However, it is also possible that the bacteria remain latent in your body for years before the infection progresses to a more serious stage. If you have active TB, you are highly likely to transmit the infection to people around you.
TB Symptoms

A person with latent TB infection doesn’t show any symptoms. Routine skin tests or blood tests can help you find out if you have latent TB. A person with Active TB may have the following symptoms:
- A persistent cough that lasts for more than 2 weeks
- Constant tiredness or fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Coughing up blood
- Fever
- Chest pain
- Chills
- Night sweats
Sometimes, Tuberculosis can attack other parts of the body, like the kidneys, brain or spine. When TB occurs outside your lungs, signs, and TB symptoms vary according to the organs involved. For instance, you may experience severe back pain when you have TB of the spine. Similarly, TB of the kidneys may cause kidney problems like blood in your urine.
Whenever you experience these symptoms, you must seek help from the specialized diagnostics department at your nearest hospital.
How is Tuberculosis Diagnosed?
Commonly, the following two tests are used to diagnose TB:
TB Skin Test
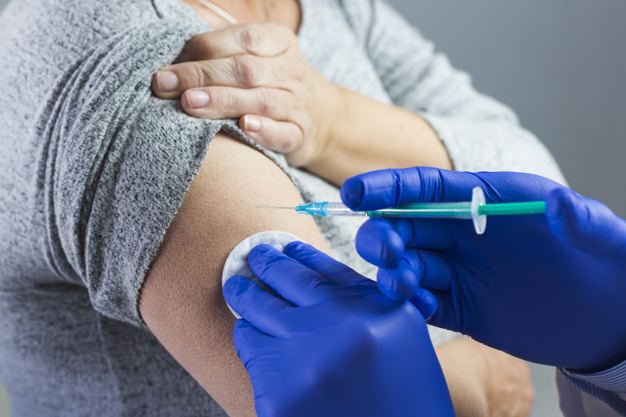
During this test, a health care worker injects a fluid into the skin on your arm. If your skin reacts to the fluid and swells up in 2-3 days after the injection, it indicates that you might have TB.
TB Blood Test
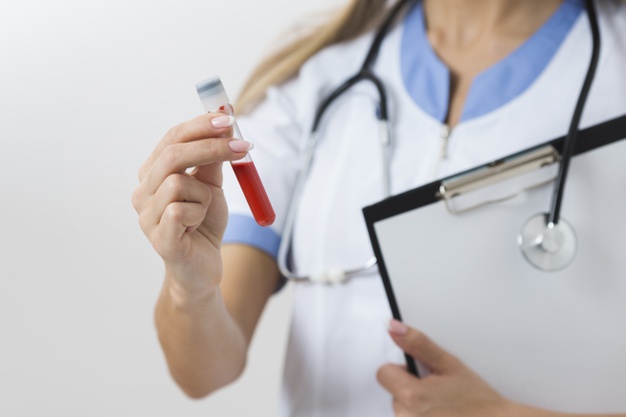

During this test, a health care worker takes some blood from your body and adds TB proteins in the collected blood. Depending upon your blood’s response to these proteins, the doctor may decide whether you are infected with the TB bacteria.
If these tests indicate that you may have active or latent TB, your doctor will further conduct X-ray examinations to identify whether your lungs or other parts of the body are affected by Tuberculosis.
Causes of Tuberculosis
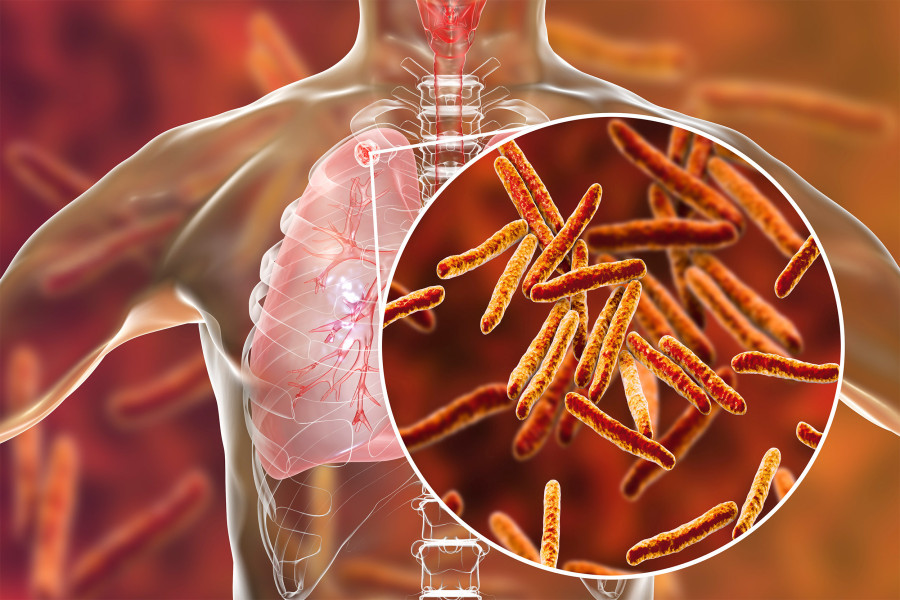
A bacteria called Mycobacterium Tuberculosis causes TB infection. These bacteria travel through the air, like the flu or cold. Tiny respiratory droplets that carry the bacteria can be released from such a person’s mouth or nose when they cough or sneeze. If you inhale these droplets, you can catch the infection.
The Mycobacterium Tuberculosis bacteria aren’t capable of surviving on surfaces. Thus, it doesn’t spread by shaking hands with the infected person or even by sharing food with them.
Tuberculosis Risk Factors
Although anyone can catch Tuberculosis, the following factors increase your risk of catching TB:
Weakened immune system
A healthy immune system often projects a strong defense against the TB bacteria. However, if you have a weak immune system, your body can’t fight the TB bacteria effectively. The following reasons may cause your immune system to weaken:
- HIV/AIDS
- Diabetes
- Certain types of cancers
- Cancer treatments, particularly chemotherapy
- Severe kidney diseases
- Malnutrition
- Recent organ transplant
Traveling to or staying in certain areas
If you stay in or travel to areas that have a history of a high number of Tuberculosis cases, you are more prone to contracting TB. Following are the areas with a comparatively high number of TB cases:
- Southeast Asia
- Africa
- Eastern Europe
- Western Pacific
- Latin America
- Caribbean Islands
Substance abuse

Excessive alcohol consumption can weaken your immune system and make you more vulnerable to Tuberculosis. Tobacco consumption has a direct impact on your lung health and smoking can cause TB.
Staying at overcrowded places
If you work at or live in a crowded place like a residential care facility, nursing homes, etc, you are at a higher risk of contracting TB from someone around you.
Tuberculosis Prevention
You must take the following prevention measures to help stop the spread of TB:
- If you are someone who suspects of having latent TB, consult a doctor and take necessary treatment to prevent active TB.
- If you are someone who lives in proximity to a TB patient, wear a mask whenever you are around them and keep washing your hands regularly.
- If you have to travel to a place where Tuberculosis is common, avoid close contact with people and get yourself tested for TB once you are back.
When To See A Doctor
TB infection, both latent and active, can potentially become life-threatening if it is not treated in time. The outlook of Tuberculosis is very good if the doctors are able to detect the disease early. So if you have been around people who have TB or if you feel the TB symptoms mentioned above, you should visit a hospital without any delay.
Regency Medical Centre provides the best treatment for TB in Tanzania. The care and treatment clinic at Regency Medical Centre provides accurate screening for TB for the right diagnosis at the right time. Our expert team of doctors provides the best medical treatment of the highest standards, along with therapeutic support, to ensure speedy recovery of all TB patients.


