World Sickle Cell Day 2020: What is Sickle Cell Disease?
734 viewsThe United Nations passed a resolution in 2008 declaring Sickle Cell Disease a public health problem. It is one of the major genetic diseases across the world, affecting millions of people annually. With an objective to raise awareness, June 19 is observed as World Sickle Cell Day. On this day, many organizations, health experts, and volunteers share information about sickle cell disease on a national and international level. This World Sickle Cell Day 2020, we are doing our bit to raise awareness through this blog. In the following sections, we explain what is sickle cell disease, sickle cell disease symptoms, and treatments.
What is Sickle Cell Disease?
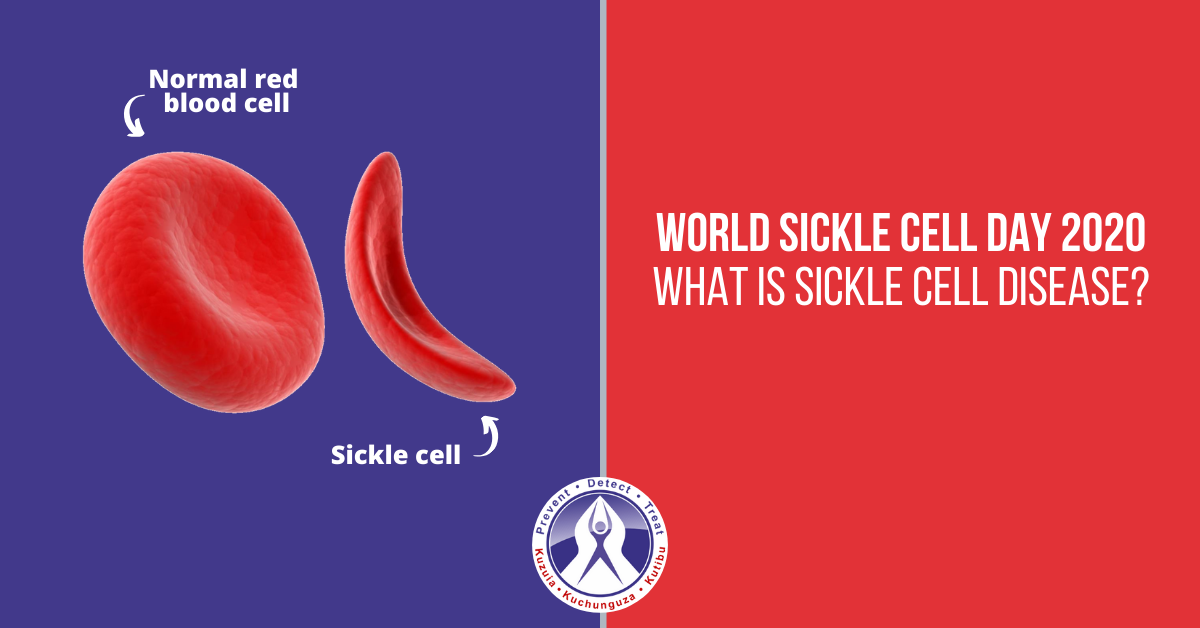
The term sickle cell disease (SCD) refers to a group of disorders that affects the red blood cells of a person. It affects haemoglobin which is mainly responsible for delivering oxygen to cells of the entire body. It is a condition in which a person has unusual haemoglobin molecules called Haemoglobin S, which can affect the form of the red blood cells.
The red blood cells are usually in the shape of round discs which makes them flexible. However, in sickle cell disease, these cells look like a crescent or an old farm tool called “sickle”. Such sickle-shaped cells get cemented together easily and cause a blockage in small blood vessels. When the blood doesn’t reach certain body parts and organs, it leads to pain and organ damage.
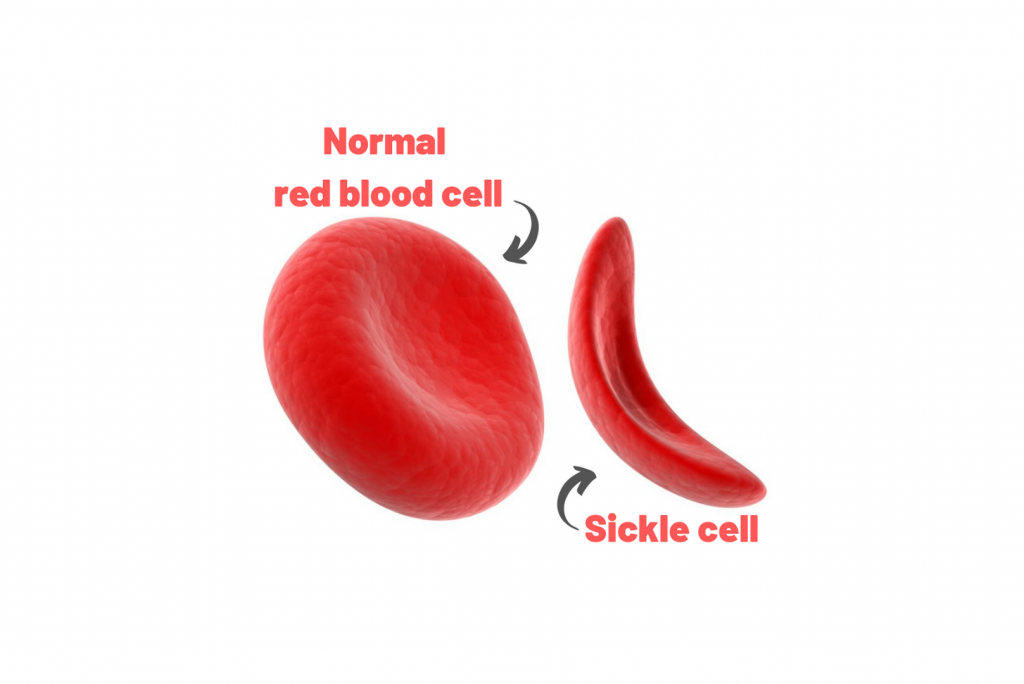 Since the sickle cells are inflexible, a majority of them disintegrate prematurely through the blood vessels. Such cells mostly last 10 to 20 days as against the normal 90 to 120 days. Your body may find it difficult to make sufficient new cells to replace the ones that you lost. This condition is known as sickle cell anaemia and it can result in shortness of breath, fatigue, and delayed growth and development in children.
Since the sickle cells are inflexible, a majority of them disintegrate prematurely through the blood vessels. Such cells mostly last 10 to 20 days as against the normal 90 to 120 days. Your body may find it difficult to make sufficient new cells to replace the ones that you lost. This condition is known as sickle cell anaemia and it can result in shortness of breath, fatigue, and delayed growth and development in children.
Sickle Cell Disease also has other medical names like HbS disease, Haemoglobin S disease, SCD, Sickle Cell Disorders.
Sickle Cell Disease Symptoms
Symptoms of sickle cell disease vary in the intensity from person to person. Here are the most common signs and symptoms that people with sickle cell disease may experience:
Anaemia
The short lifespan of sickle cells causes anaemia. It makes a person feel dizzy and very tired.
Severe Pain
Sickle cells have a tendency to get stuck together in blood vessels which creates a blockage and jams the blood flow resulting in severe pain. One can experience pain anywhere, more commonly in the chest, arms, and legs. Infants and young children may also experience painful swelling of the fingers and toes.
Acute Chest Syndrome
It occurs when the sickling of the cells takes place in the chest. It happens suddenly and can be life-threatening. The sickle cells obstruct the flow of oxygen in the tiny vessels in the lungs and induce fever, pain, and a violent cough.
Splenic Sequestration or Pooling
This is a condition in which a large number of sickle cells are trapped in the spleen. The spleen can grow larger and painful due to a rise in the blood volume and malfunction. If the episodes are recurrent, the spleen becomes scarred and permanently damaged. This can be a life-threatening condition if not treated immediately.
Stroke
Another impetuous and serious complication of sickle cell disease can be a stroke. Sickle cells can clog the major blood vessels that supply oxygen to the brain. The consequence can be severe brain damage.
Jaundice
It is a fairly common symptom. Sickle cells break down even before the liver can filter them out. Subsequently, Bilirubin (which causes the yellow color) from these broken cells accumulates in the system causing jaundice.
Priapism
This is a very painful condition in which the blood vessels in the penis are jammed by the sickle cells. It can lead to impotence in males if not taken care of promptly.
Causes of Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease is a hereditary blood disorder resulting from a defective gene.
A person will be diagnosed with SCD at birth, only if he/she inherits two genes – one from the mother and one from the father.
If a person inherits just a single gene from either parent then he/she is healthy but is said to be a ‘carrier’ of the disease. A carrier has a greater probability of having a child with sickle cell disease if he/she conceives a child with another carrier.
For parents who are each carrier of a sickle cell gene, there is a 25% chance of having a child with SCD.
How is Sickle Cell Disease Diagnosed
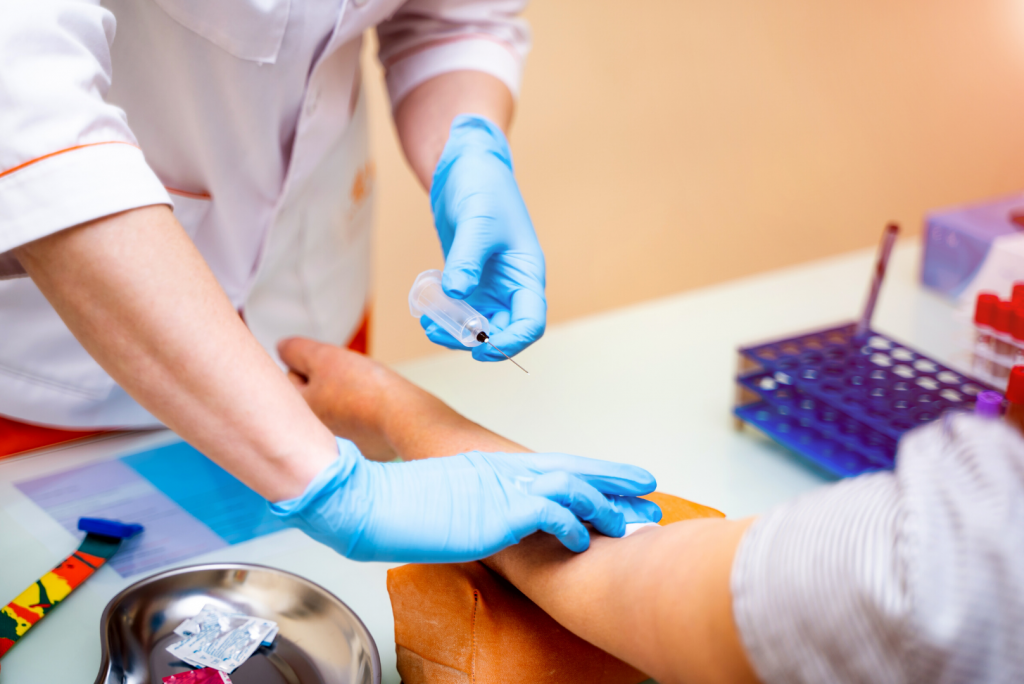
In order to diagnose whether a person is a carrier of a sickle cell, doctors administer Haemoglobin Electrophoresis blood test. The same test can help the parents find out how likely it is that their children will have SCD.
Complications of Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease creates problems for any and all major organs of our body. The liver, heart, kidneys, gallbladder, eyes and joints can undergo damage from the atypical function of the sickle cells and their inadequacy to smoothly flow through the small blood vessels properly. Complications may include the following:
- Increased infections
- Leg ulcers
- Bone damage
- Kidney damage and loss of body water in urine
- Multiple organ failure
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment
As of now, the only cure for sickle cell disease is stem cell transplant (bone marrow transplant). This treatment is very risky and involves a very complex procedure. Only some patients have an option to go for this treatment.
Scientists are also studying gene therapy as a means of treatment for sickle cell anaemia. Their objective is to eliminate the disease by altering or replacing the normal gene that causes it.
However, despite the unavailability of a cure, people with sickle cell disease can lead fairly normal lives with a proper treatment plan which might involve:
- Immunizations and daily doses of penicillin so as to avoid infection. In addition to all the appropriate childhood vaccinations, teens with sickle disease should get the pneumococcal, flu, and meningococcal vaccines.
- Include folic acid supplements in the medication to help make new red blood cells and other necessary medications required to subside the pain.
- Getting blood transfusion.
Conclusion
Unfortunately, the treatment for sickle cell disease is not one that’s easy and the disease can last for a lifetime. Although, a person cannot get rid of the complications entirely, leading a healthy life can make things a lot easier for a patient suffering from sickle cell disease.
It is essential that people with sickle cell disease have a healthy diet which consists of a lot of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and protein. They must also drink plenty of fluids.
One must prevent infections by getting an annual flu shot, washing hands more often, and getting frequent dental exams.