All You Need to Know About Cervical Cancer
786 views The fourth most common cancer in women, cervical cancer has created havoc. This cancer usually develops in a woman’s cervix and 99% are linked to infection due to HPV. It is frequently diagnosed in women of the age range of 35 to 44. This rarely develops in women less than age 20. Cancer is named based on where it starts. As this type of cancer originates at the cervix, it is known as cervical cancer.
The fourth most common cancer in women, cervical cancer has created havoc. This cancer usually develops in a woman’s cervix and 99% are linked to infection due to HPV. It is frequently diagnosed in women of the age range of 35 to 44. This rarely develops in women less than age 20. Cancer is named based on where it starts. As this type of cancer originates at the cervix, it is known as cervical cancer.
Here we have listed the entire details about the symptoms, stages, causes and prevention of cervical cancer.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
We often experience certain pain and discomfort in our daily lives. But we tend to ignore that it might be something serious and lead to severe health conditions.
 Like many other diseases, cervical cancer symptoms are equivalent to zero in the early stages. But, at later stages, the most common symptoms are:
Like many other diseases, cervical cancer symptoms are equivalent to zero in the early stages. But, at later stages, the most common symptoms are:
- Pelvic pain
- Pain during intercourse
- Bleeding post-menopause
- Blood along with vaginal discharge
- Strong odour with vaginal discharge
- Bleeding between periods
These symptoms are also observed when someone is having a urinal infection. But, in either case, it is highly recommended to visit a doctor and undergo a checkup.
Stages of Cervical Cancer
The stages of cancer are usually determined based on the spread of the cancer cells as well as their severity. This also helps the doctors to understand what type of treatment will be most effective.
The stages of cervical cancer are as follows:
Stage 1
If cancer has spread from the cervix lining into the deeper tissue, but at the same time is still just found in the uterus, it can be defined as stage 1 of cancer. Here, it has not spread to other parts of the body. The further classification of stage 1 are as follows:
Stage 1A: Diagnosed only by viewing cervical tissue or cells under a microscope. Imaging tests or evaluations of tissue samples can also be used to determine tumour size.
Stage 1A1: Cancerous area of fewer than 3 mm in depth.
Stage 1A2: Cancerous area 3 mm to less than 5 mm in depth.
Stage 1B: Here, the tumour is larger but still only confined to the cervix. There is no distant spread.
Stage 1B1: Tumour is 5 mm or more in-depth and less than 2 cm wide.
Stage 1B2: Tumour is 2 cm or more in-depth and less than 4 cm wide.
Stage 1B3: Tumour is 4 cm or more in width.
Stage 2
When cancer has spread beyond the uterus to nearby areas, such as the vagina or tissue near the cervix, but it is still inside the pelvic area, it is stage 2 of cervical cancer. Even now, it has not spread to other parts of the body. It can be further classified as follows:
Stage 2A: Tumour is limited to the upper two-thirds of the vagina. It has not spread to the tissue next to the cervix, which is called the parametrial area.
Stage 2A1: Tumour is less than 4 cm wide.
Stage 2A2: Tumour is 4 cm or more in width.
Stage 2B: Tumour has spread to the parametrial area.
Stage 3
When the tumour involves the lower third of the vagina and spreads to the pelvic wall, causing swelling of the kidney, it is stage 3. There is no distant spread.
Stage 3A: Tumour involves the lower third of the vagina, but it has not grown into the pelvic wall.
Stage 3B: Tumour has grown into the pelvic wall and/or affects a kidney.
Stage 3C: Tumour involves regional lymph nodes.
Stage 3C1: Cancer starts spreading lymph nodes in the pelvis.
Stage 3C2: Cancer spreads to para-aortic lymph nodes.
Stage 4
The last stage and one of the most deadly stages of cancer is stage 4 of cervical cancer.
Stage IVA: Cancer has spread to the bladder or rectum, but it has not spread to other parts of the body.
Stage IVB: Cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Causes
When there’s an uncontrolled division and growth of abnormal cells in the body, these cells add up to form a lymph or tumour. Scientists are unsure about how these cell clusters turn cancerous, but this is what leads to cancer. Specifically for cervical cancer, these are the probable causes:
- Birth control pills: Excessive or long term use of these pills can lead to causing cancer.
- Other STDs: Chlamydia, gonorrhoea, syphilis or the presence of other STDs can lead to causing cancer.
- Weakened immune system: People who have had HIV or transplants have higher risks of getting cervical cancer.
- Sexually active since early ages: It has been observed that women who are sexually active since early ages or have multiple partners, might get cervical cancer.
- Smoking: Smoking not only increases the risk of cervical cancer but also leads to higher chances of developing other cancerous cells too.
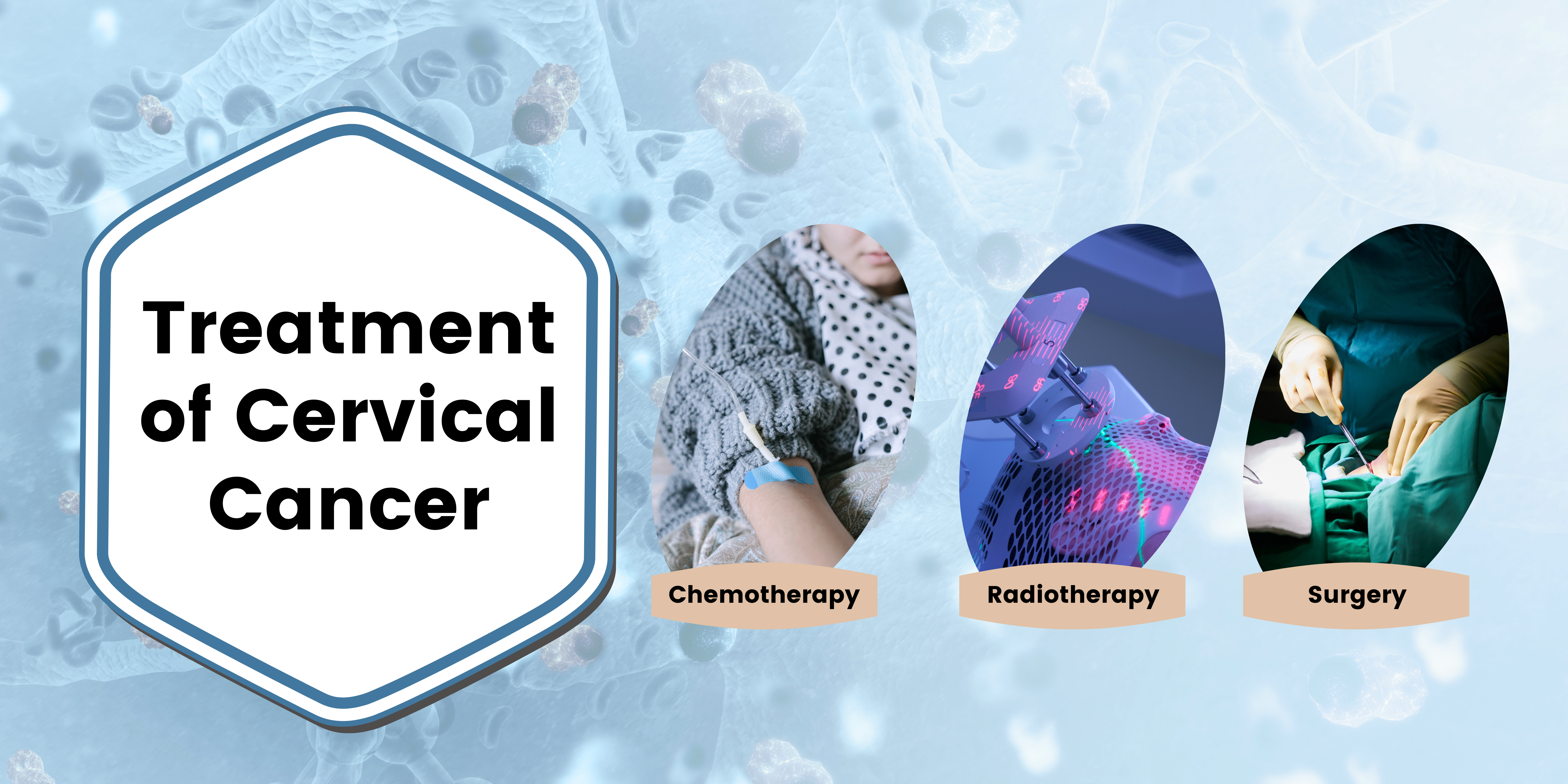
Treatment
The treatment of cervical cancer depends on several factors, including the stage of cancer, your overall health and age. Doctors suggest that it is easier to treat cancer when diagnosed at an early stage. The other treatment options include:
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is a renowned cancer treatment in which doctors target cancerous cells using chemicals. Usually, the cancerous cells which did not get removed in surgery or can’t be removed using surgery are targeted with this treatment.
- Radiotherapy: In radiotherapy, beams of high-energy X-rays are used to destroy the cancer cells. The doctor aims the rays around the pelvic area where these cancerous cells are existing to destroy them.
- Surgery: Surgery is a very common treatment, but it only works when cancer has not spread from the cervix. Also, it only works when the cancer is at an early stage.
 Our unhealthy lifestyle choices are leading us to several diseases. The increasing number of cervical cancers is one of them. This all can be avoided by also scheduling regular health checkups and following the doctors’ advice.
Our unhealthy lifestyle choices are leading us to several diseases. The increasing number of cervical cancers is one of them. This all can be avoided by also scheduling regular health checkups and following the doctors’ advice.
At Regency Medical Centre, we have experts and healthcare professionals that are sound to diagnose and treating enumerated diseases. We also have cervical cancer screening cells for the early diagnosis and prevention of the same. You can get in touch with us to schedule your appointment.

