AN ENTIRE GUIDE TO HYDROCELE IN CHILDREN!
1,091 viewsHydrocele is not an alien condition, in fact, statistics say that 10% of male children are born with hydrocele. Since we are aware that it is not an unknown, unheard kind of situation, thus it is an important subject matter for discussion.
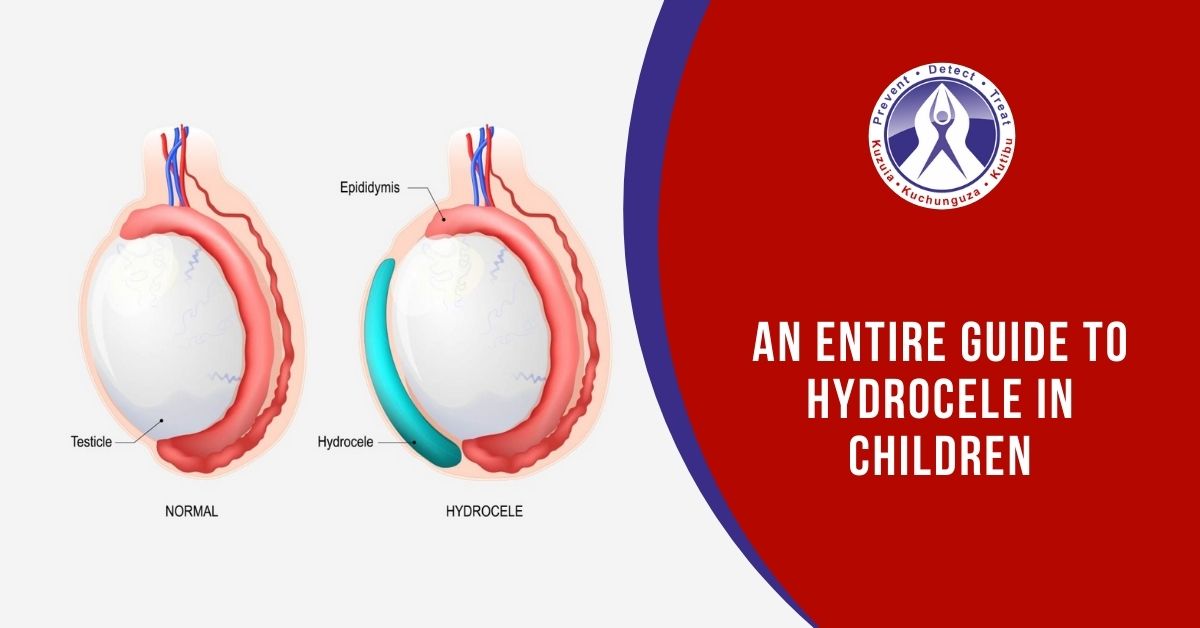
Hydrocele is basically swelling in the scrotum due to the accumulation of fluid in the sheet covering the testicles. A general observation says that it is most common among infants, but there is a fair chance that it could happen to older people as well because of any injury in or within the scrotum.
HOW DOES THIS CONDITION DEVELOP?
The primary reason is fluid accumulation around testicles. When the baby is in mother’s womb, a sac or pouch is developed, which slowly descends into the scrotum with the testes. However, it can still take up two different courses of action based on its different types:
Types of Hydrocele based on opening or closing of sac-
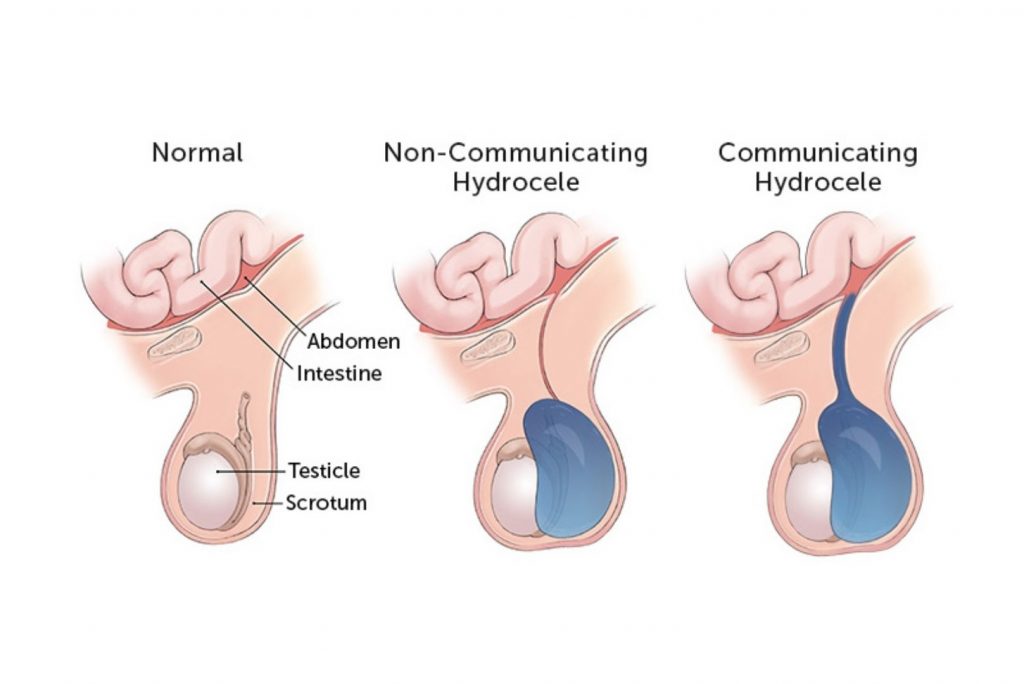
1. non-communicating hydrocele
where the fluid remains sealed inside the sac and the body does not come in contact with it. Here, the fluid gradually absorbs and goes away on its own within a year. But there exists a considerable chance of an infection or a condition is observed in an older child.
2. Communicating hydrocele
In communicating hydrocele, the sac is not completely closed off and the fluid keeps on moving in and out of the sac. This results in changes in the size of hydrocele when the scrotal sac is compressed causing the fluid to flow back to the abdomen as compared to when the sac is relaxed.
Types of Hydrocele based on Age
1.Infantile
Observed mostly in infants and common in nature and generally gets dissolved within the first year of an infant’s birth. In case it is still there, an immediate appointment or consultation with the pediatrics or urologist is required.
2. Adult-onset
Found in slightly younger boys and men. It can arise at any instance during the lifetime.
HOW TO IDENTIFY THE RED FLAGS?
Symptoms of Hydrocele might vary from child to child but some of these include:
- Typically a swelling that is smooth and not painful.
- Scrotum that usually gets smaller at night while lying flat, and bigger during activity.
- Extreme scrotal pain.
- Hydrocele generally gets dissolved in babies with 12-18 months, but if the case is not, then immediately consult the doctor.
Now that we have a fair share of understanding as to what hydrocele is, let us jump on to the surgical procedures adopted by the doctors: HYDROCELECTOMY!
Hydrocelectomy is a kind of surgery done to repair a build-up of fluid around a testicle in cases where hydrocele grows larger causing swelling, pain, and discomfort. In hydrocelectomy, fluid is extracted which eventually shrinks the size of the sac.
PRE-SURGERY STEPS
There will be standard preoperative blood and urine tests conducted to assess the present status and opt for a specific course of operation. A proper briefing session will be conducted addressing the procedure and questions like the time frame of the surgery, incision, and any other queries that the patient might have. This assists with forestalling disease and the development of liquid in the scrotum after a medical procedure.
A patient should or the parent in the case of an infant should be completely vocal about all the medications, dietary intake, and rest of the health-related concerns to the doctor because in many cases, your consumption habits can lead to extreme complications like bleeding and clotting. An infant’s diet before the surgery should be strict as per the prescription of the pediatrician.
STEPS CONDUCTED IN HYDROCELECTOMY
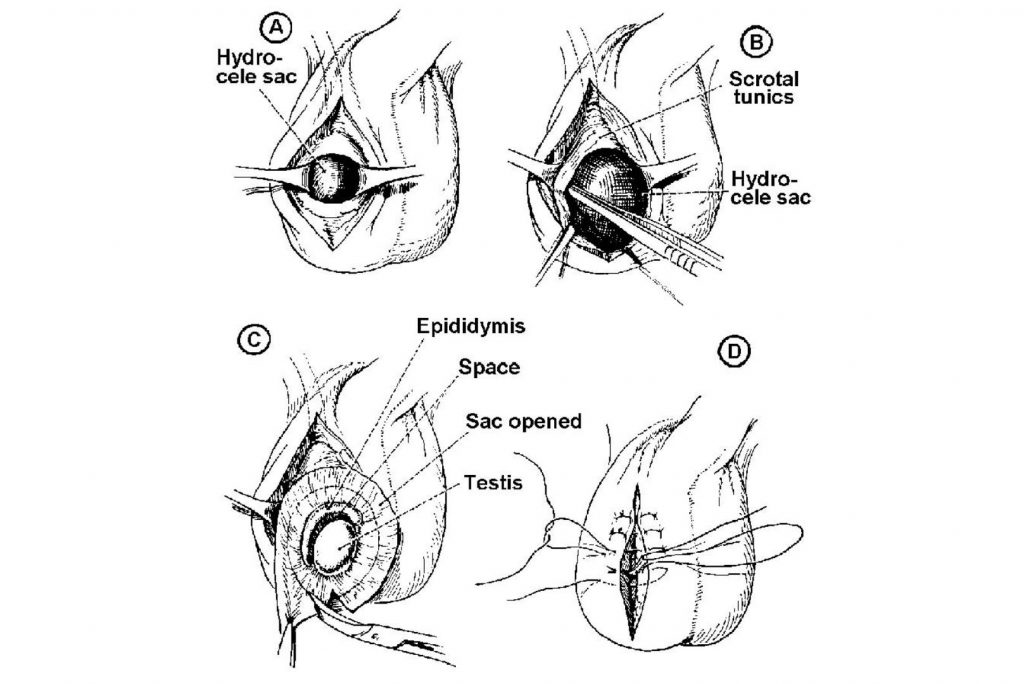
An aware patient must always know the periphery of the medical procedure to be conducted. Here is a glimpse of it:
Primary information states that it is an outpatient surgery and requires general anesthesia so that the patient will be completely unconscious during the entire procedure. The patient’s breathing is regulated by inserting a small tube through the throat. Before the medical procedure, you’ll have an intravenous line placed in your arm to give liquids and any medicine required. The major step of the surgery is where the surgeon makes a small incision in the scrotum and with the help of suction, drains out the fluid from the scrotum or the hydrocele.
Depending upon case to case, sometimes doctors even use a laparoscope which is basically a tube with a tiny camera at the end. This is a minimally invasive procedure where the surgeon can view the inside of the patient’s scrotum on an external video monitor. Small instruments are then inserted by making a keyhole incision and the damage is taken care of.
RECOVERY AND PRECAUTIONS AFTER THE HYDROCELECTOMY
To ensure that there is no unusual after-effects post-surgery, the doctors will take the patient to an observation room. This is an important step after the surgery since the patient was on sedatives, making him nauseous. The patient is then permitted to go home once their senses are back to normal.
- There might be swelling and soreness for a month. To reduce the swelling, apply cold packs for 10-15 minutes every day for the first few days.
- The scrotum will be bandaged using a jockstrap for support and reduces discomfort. Avoid the bandage from any kind of soaking. Showering with the bandaged area covered is permissible.
- Avoid any kinds of heavy lifting or vigorous exercise during the recovery.
And just like that, in a few weeks, the patient will be good to go.
Lastly, Hydrocele is a curable condition. With proper care and awareness, one can easily identify the symptoms and treat them well in advance. If neglected can turn up to dangerous testicular conditions that might cause serious complications. Parents must be very cautious with infants because they can’t talk so regular health check-ups with the pediatrician and urologists are advisable to ensure a healthy and sound body.
Our team is here to help you out with consultation. So for any queries or appointment inquiries.