Biopsy: How It’s Used to Diagnose Cancer
807 viewsIf your doctor finds something suspicious during your regular physical examinations or if they see certain cancer-related symptoms in your body, they may ask you to get a biopsy done. There are many other tests that may indicate that cancer is present. These tests are able to spot tumor markers but they aren’t diagnostic tests. Only a biopsy procedure is used to diagnose cancer.
What is a biopsy?
A biopsy is a procedure during which a doctor removes a small piece of tissue or a sample of cells from the patient’s body. A pathologist then examines the sample tissue to check whether any cells are abnormal.
Types of Biopsy Used to Diagnose Cancer
The type of biopsy procedures your doctor will ask you to undergo depends on the location of the possible tumor.
Needle Biopsy
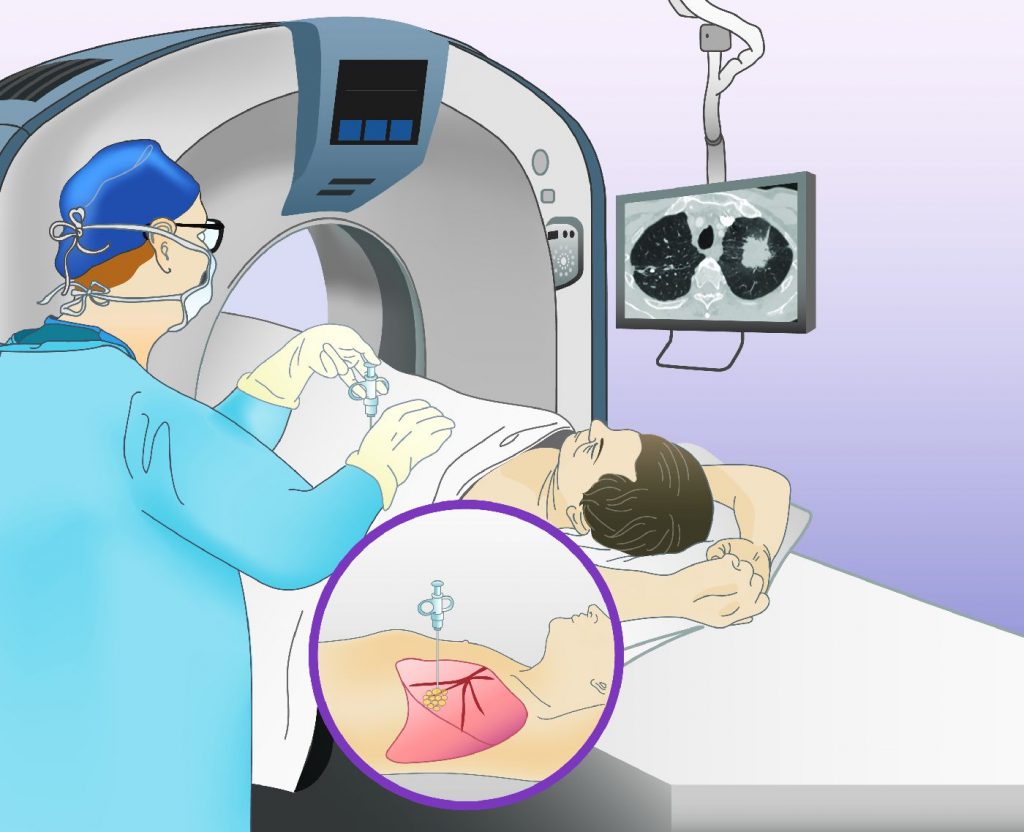 When a doctor suspects a tumor by touching the skin, they use a needle to take out the sample tissue from the affected area. Even when the lump or mass cannot be felt, the doctors can do an image-guided needle biopsy to locate where the mass is and to take it out.
When a doctor suspects a tumor by touching the skin, they use a needle to take out the sample tissue from the affected area. Even when the lump or mass cannot be felt, the doctors can do an image-guided needle biopsy to locate where the mass is and to take it out.
There are 2 types of needle biopsy:
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)
In fine needle aspiration, the doctor uses a thin needle attached to a syringe to take out a small portion of fluid and tissue from the suspicious mass. Fine needle aspiration is considered the best biopsy to diagnose cancer because the skin isn’t cut during this procedure. The reports of FNA biopsy can take two to three days to reach the patient.
Core Needle Biopsy
Doctors use larger needles to carry out core needle biopsy. In this procedure, they take out a comparatively bigger, cylindrical portion of the suspicious tissue. The doctors give local anaesthesia to the patients before performing core needle biopsy.
Depending upon the type of cancer, the doctor may also use a special vacuum tool to take out multiple or larger samples of the tissue. The process of examining core needle biopsy is longer than a fine needle biopsy.
Excisional Biopsy and Incisional Biopsy
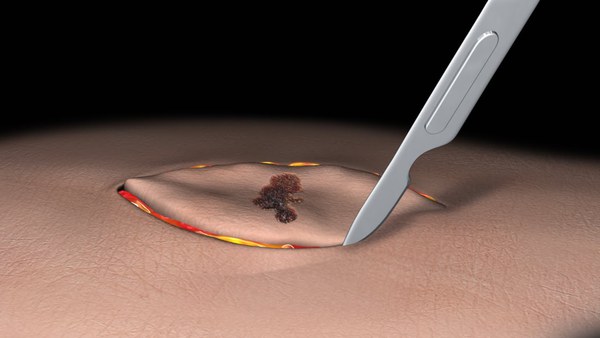
In certain cases, the doctors may consider surgically removing the entire mass of affected tissue or a large part of it by cutting through the skin. They also remove some normal areas around the tumor to ensure that the tumor hasn’t spread further. In an excisional biopsy, the doctor removes the entire tumor whereas, in an incisional biopsy, they don’t take out the entire tumor. If excisional biopsy leaves a wide wound on the skin, the doctor may perform skin grafting. Skin grafting is a process in which the doctor fills up the gap in the skin with skin from another body part. However, in most cases, the doctor can bind the wounded skin just by using stitches. All patients need local anaesthesia during these processes.
Skin Biopsy
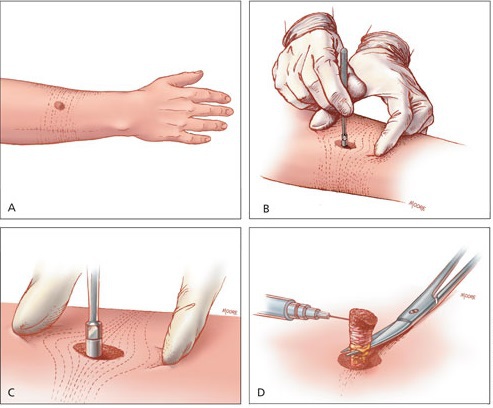
Doctors recommend a skin biopsy to diagnose cancer when there is a rash or lesion on the skin which the medications aren’t able to cure and the cause of which is unknown. Depending upon the type of tumor, the doctor may perform one of the following types of skin biopsy:
- Shave biopsy during which the doctor scrapes the surface of the skin using a tool similar to a razor
- Punch biopsy during which the doctor removes a section from the deeper layers of skin using a circular tool called punch
- Incisional biopsy during which the doctor cuts out a small portion of your skin using a scalpel
- Excisional biopsy during which the doctor removes the entire mass of the lump
All the types of skin biopsy are performed under the effect of local anaesthesia.
Endoscopic biopsy
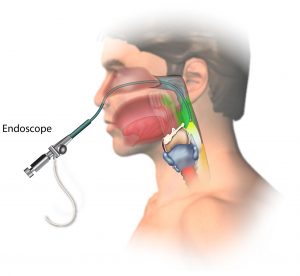 An endoscope is a thin tube that has a video camera or a lens at its bottom end. During an endoscopic biopsy, the doctor looks inside various parts of the body using this tube to search for tumors. After locating the lump, they also take out a specimen using the same tube. Different types of endoscopic biopsy are done to look inside different parts of the body. For example, the doctor performs a cystoscopy to collect tissue samples from the bladder and bronchoscopy for lungs. Depending upon the type of endoscopy to be carried out, the doctor may give the patient a sedative or anaesthesia to numb their pain.
An endoscope is a thin tube that has a video camera or a lens at its bottom end. During an endoscopic biopsy, the doctor looks inside various parts of the body using this tube to search for tumors. After locating the lump, they also take out a specimen using the same tube. Different types of endoscopic biopsy are done to look inside different parts of the body. For example, the doctor performs a cystoscopy to collect tissue samples from the bladder and bronchoscopy for lungs. Depending upon the type of endoscopy to be carried out, the doctor may give the patient a sedative or anaesthesia to numb their pain.
Surgical biopsy
Sometimes it’s not possible to safely access the tumor using the above types of biopsy. In that case, the doctor performs a surgical biopsy using different tools to take a specimen from the questionable mass. For example, laparoscopic surgery is a procedure during which the doctor cuts through the abdomen to look inside and take out a sample of abnormal tissue. Thoracoscopy is another type of surgical biopsy to access susceptible mass inside the lungs. Since surgical biopsy essentially cuts through a body part, the doctor always gives general anaesthesia to the patient so they are in deep sleep during the surgery. The doctor may also keep the patient under observation for a day after the surgical biopsy. They may do so to ensure that the patient’s body hasn’t caught any infection during the surgical biopsy.
What happens after a biopsy
After the doctor has taken out a sample of the suspicious tissue, they send the tissue to a pathological lab. Based on the type of biopsy carried out, the tissue sample may either be chemically treated or may be frozen and sliced into fine sections. The pathologist then places these sections a glass slide and study them under a microscope to check whether the cells in the tissue are malignant (cancerous). If the cells are malignant, the biopsy report can tell your doctor the origin, type, and stage of cancer. The doctor then guides you on the best course of action for treating cancer.
Other times, the report indicates that the cells of the tissue sample are benign (non-cancerous). In that case, your doctor may suggest the right options to consider for treating the abnormality of the tissue.
Sometimes your doctor may not fully trust the negative biopsy report (non-cancerous). In such cases, they may ask you to get a different type of biopsy done. It is important to make sure that the abnormal tissues in your body are non-cancerous.
A surgical biopsy procedure may also be a live biopsy. In such types of biopsy, a pathologist examines the sample cells immediately. The results are available to your doctor within minutes. However, in most cases, it may take a few days for the doctor to get the biopsy reports. After performing the biopsy, your doctor will let you know when you can expect the reports.
It’s advisable to read about biopsy a bit and ask your doctor all the doubts you may have regarding it. You can write down the questions prior to the appointment so that you don’t miss out on any questions.
Regency Medical Centre has carried out over 30,000 endoscopic investigations and over 10,000 endoscopic surgeries to date. With the help of highly advanced equipment, our team of super-specialized doctors is known for providing the best endoscopy in Dar es Salaam and all over Tanzania. Please visit https://www.regencymedicalcentre.com/endoscopy/ to know more.


